As the digital landscape becomes more integral to business operations, the responsibilities of a Chief Financial Officer (CFO) have expanded beyond traditional financial oversight. One area that garnered significant attention is mitigating risks associated with digital Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) lawsuits. These lawsuits are on the rise and pose a legal threat as well as a financial and reputational one. For CFOs in Corporate America, understanding how to navigate these risks is crucial.
The Rise of Digital ADA Lawsuits
The ADA was enacted in 1990 to ensure equal access to public spaces for individuals with disabilities. While initially focused on physical locations, the ADA has evolved to include the digital realm. As more businesses operate online, websites and mobile applications are increasingly considered “public spaces” under the ADA. Companies must ensure that their digital platforms are accessible to people with disabilities.
Failure to comply with these requirements can result in costly lawsuits. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in digital ADA lawsuits, with thousands of cases filed annually. These lawsuits often target companies with websites or apps that are not accessible to individuals with disabilities, such as those with visual, auditory, or cognitive impairments.
Why CFOs Should Be Concerned About ADA Lawsuits
CFOs are responsible for managing their organization’s financial health, which includes mitigating risks that could lead to financial loss. Digital ADA lawsuits represent a significant risk for several reasons:
- Financial Penalties: Non-compliance with ADA requirements can result in substantial fines and legal fees. These costs can quickly escalate, mainly if a company is involved in multiple lawsuits. For example, businesses that violate Title III of the ADA may face a maximum civil penalty of $75,000 for a first violation. Subsequent violations have been seen with up to a $150,000 fine.
- Reputational Damage: In today’s socially conscious environment, failing to provide accessible digital experiences can harm a company’s reputation. Negative publicity from an ADA lawsuit can lead to losing customer trust and loyalty, ultimately affecting the bottom line.
- Operational Disruption: ADA lawsuits can be time-consuming and disruptive to business operations. Companies may need to divert resources to address the legal proceedings and change their digital platforms.
- Market Competitiveness: Companies prioritizing digital accessibility are better positioned to reach a broader audience, including the estimated 26% of the U.S. population living with a disability. This can provide a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Critical Steps to Mitigating Digital ADA Lawsuit Risks
CFOs are critical in mitigating the risks associated with digital ADA lawsuits. They can help protect their organization from legal action by taking proactive steps and ensuring compliance with ADA requirements. Here are the key steps CFOs should consider:
Conduct a Comprehensive Accessibility Audit
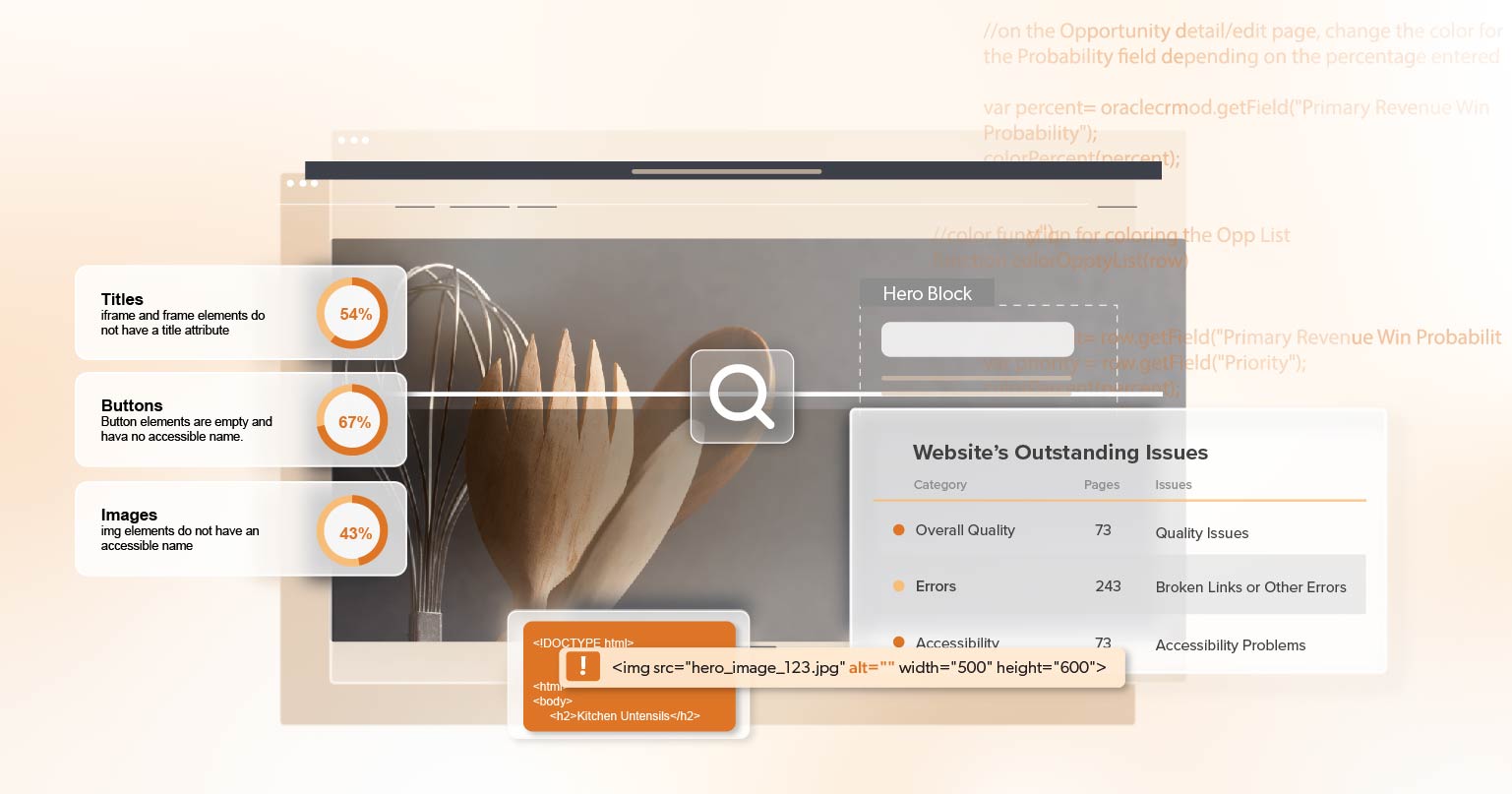
The first step in mitigating ADA risks is to understand the current state of your organization’s digital accessibility. This involves conducting a comprehensive accessibility audit of your website, mobile apps, and other digital platforms. An audit will identify areas where your digital assets fall short of ADA compliance and provide a roadmap for remediation.
There are different types of accessibility audits, ranging from automated scans to manual testing by accessibility experts. While automated tools can quickly identify some issues, manual testing is essential for detecting more nuanced problems that automated tools might miss. A combination of both methods is often the most effective approach.
Implement a Remediation Plan
Once the audit is complete, the next step is implementing a remediation plan to address the identified issues. This plan should prioritize the most critical accessibility barriers and outline a timeline for making the necessary changes. It’s essential to involve key stakeholders, including web developers, content creators, and legal teams, in the remediation process to ensure that all aspects of digital accessibility are covered.
Establish Ongoing Monitoring and Maintenance
Digital accessibility is not a one-time project; it requires ongoing monitoring and maintenance. As your organization updates its digital platforms, new accessibility issues may arise—regular accessibility audits and monitoring tools, such as 216digital‘s a11y. Radar can help ensure that your digital assets remain compliant over time.
Ongoing monitoring is also essential for preventing frivolous ADA lawsuits. By maintaining a high level of digital accessibility, your organization can demonstrate its commitment to compliance, making it less likely to be targeted by opportunistic lawsuits.
Integrate Accessibility into Your Business Strategy
CFOs should advocate for integrating digital accessibility into the broader business strategy. This includes incorporating accessibility considerations into the design and development processes of new digital products and services. By making accessibility a core component of your organization’s digital strategy, you can reduce non-compliance risk and create a more inclusive user experience.
Stay Informed About Legal Developments
The legal landscape surrounding digital ADA compliance is continually evolving. CFOs must stay informed about changes in regulations, court rulings, and best practices for digital accessibility. This knowledge will enable you to anticipate potential risks and proactively mitigate them.
Partnering with legal experts who specialize in ADA compliance can also be beneficial. These professionals can guide the latest developments and help ensure your organization’s digital assets align with current legal requirements.
Build a Culture of Accessibility
Finally, fostering a culture of accessibility within your organization is critical to long-term compliance. This means educating employees about the importance of digital accessibility and providing them with the tools and training they need to create accessible content and experiences.
CFOs can lead by example by championing accessibility initiatives and allocating the necessary resources to support them. By embedding accessibility into your organization’s culture, you can create a sustainable approach to compliance that extends beyond the minimum legal requirements.
Wrapping Up
As CFOs in Corporate America, mitigating the risk of digital ADA lawsuits is a critical responsibility. By conducting thorough accessibility audits, implementing effective remediation plans, establishing ongoing monitoring, and integrating accessibility into the business strategy, CFOs can protect their organizations from legal, financial, and reputational harm. Moreover, by building a culture of accessibility, they can position their companies as leaders in inclusivity, ultimately driving long-term success.
Digital accessibility is not just a legal obligation; it’s a business imperative to enhance your company’s reputation, expand its customer base, and ensure compliance in an increasingly complex regulatory environment. Taking proactive steps today can save your organization from costly lawsuits and contribute to a more inclusive digital world for everyone.
Ready to take the next step? Schedule a complimentary ADA Strategy Briefing with 216digital today and start building a more accessible future for your company.